PPT GENOME MAPPING PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5876156
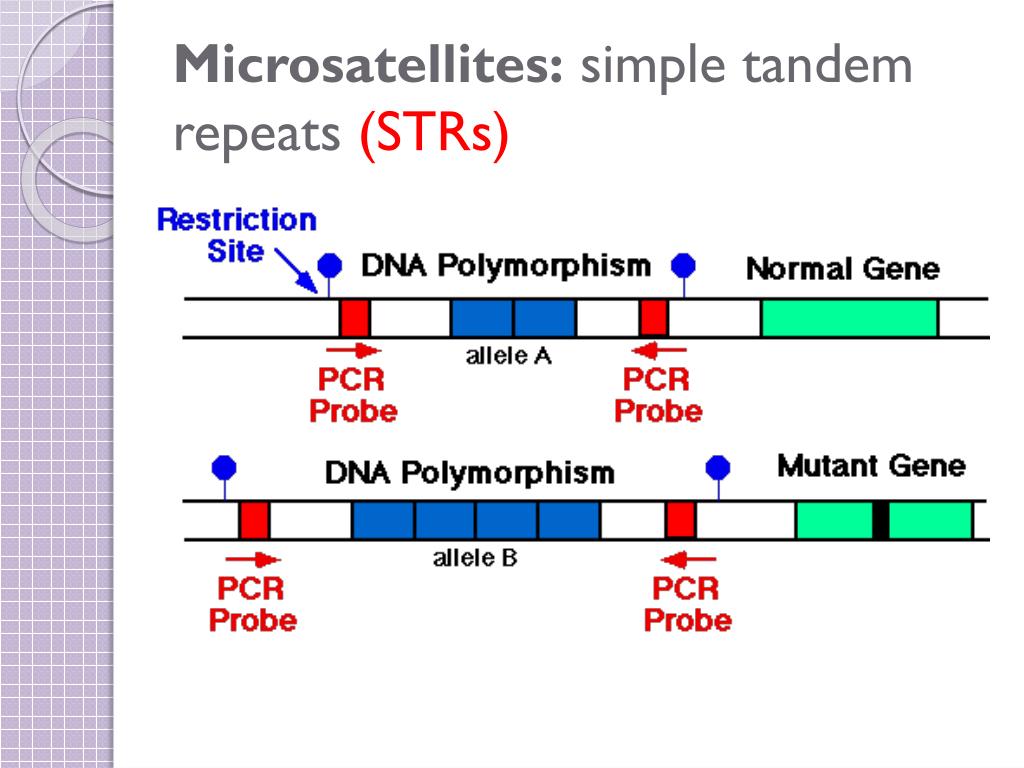
Two classes of tandem repeat sequences, minisatellites and microsatellites, have gained increasing attention from the scientific community over the past decade. Microsatellites are tandem arrays of short (usually <10 bp) units, while minisatellites are tandem arrays of longer units (>10 and <100 bp). These two kinds of sequence are widespread.
Teorica 3 1 Alumnos Em

Molecular markers and its application in animal breeding. Reshma Raj S , D.N. Das, in Advances in Animal Genomics, 2021. 9.3.5 Minisatellites. A minisatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs (ranging in length from 10 to 60 base pairs) are typically repeated 5-50 times. Minisatellites are notable for their high mutation rate and high diversity in the population, and.
Ciencias de Joseleg Ubicación y función del ADN microsatélite

It usually repeats 5 to 50 times. These minisatellites are more distinguished in the telomeres and the centromeres of the chromosome. This small sequence of repetitive DNA does not code for any protein. Minisatellites, along with microsatellites, are termed VNTR (variable number tandem repeats). Sometimes minisatellites alone are referred to as.
PPT Searching Microsatellite Markers for Mapping a Disease Gene PowerPoint Presentation ID
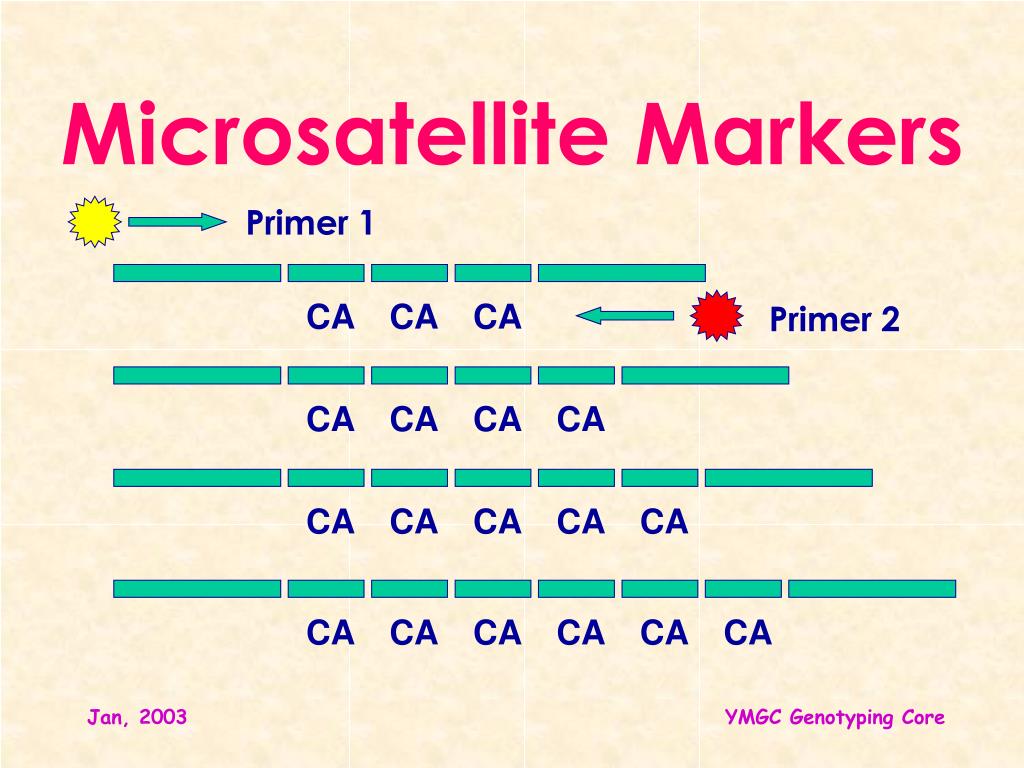
Microsatellite DNA is common in all organisms that have been evaluated but differ in number, size, and distribution (Chambers and MacAvoy, 2000; Rakoczy-Trojanowska and Bolibok, 2004).Microsatellites are composed of tandemly arranged repetitive DNA sequences (generally four to six nucleotides) up to a kilobyte in length (Fig. 33), most frequently located in untranslated regions (UTRs) and are.
What is the Difference Between Microsatellite and Minisatellite
Background. Microsatellites, also termed as simple sequence repeats (SSRs), are short tandemly repeated sequences with 1-to-6 base pair (bp) motifs [1, 2].They are ubiquitous and highly abundant in eukaryote, prokaryote and virus genomes [3-5], making up around 3% of the human genome [].Microsatellite instability is an important and unique form of mutation that is responsible for, or.
IJMS Free FullText Sequence, Chromatin and Evolution of Satellite DNA
One major exception is DNAfingerprinting and the subsequent variations in mini/microsatellite applications. The discovery of minisatellite DNA fingerprinting by A. Jeffreys in 1985 ( Jeffreys et al. 1985a, Jeffreys et al. 1985b) in one brief step revolutionised the way forensic science and police casework is performed, and became the norm for.
Frontiers Functional Significance of Satellite DNAs Insights From Drosophila
This applies both to longer repeated sequences, minisatellites (about 10-100 base pairs), and microsatellites (mostly 2-4 base pairs). Although these satellite DNAs are abundantly distributed in all kinds of organisms, no clear function has been discerned for them. However, extension of trinucleotide microsatellite sequences has been associated.
PPT Genomics PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID721868
Other articles where microsatellite DNA is discussed: heredity: Repetitive DNA: Microsatellite DNA is composed of tandem repeats of two nucleotide pairs that are dispersed throughout the genome. Minisatellite DNA, sometimes called variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs), is composed of blocks of longer repeats also dispersed throughout the genome. There is no known function for satellite…
DNA profiling for dogs and cats what is it and what is it for? AnimaLabs©

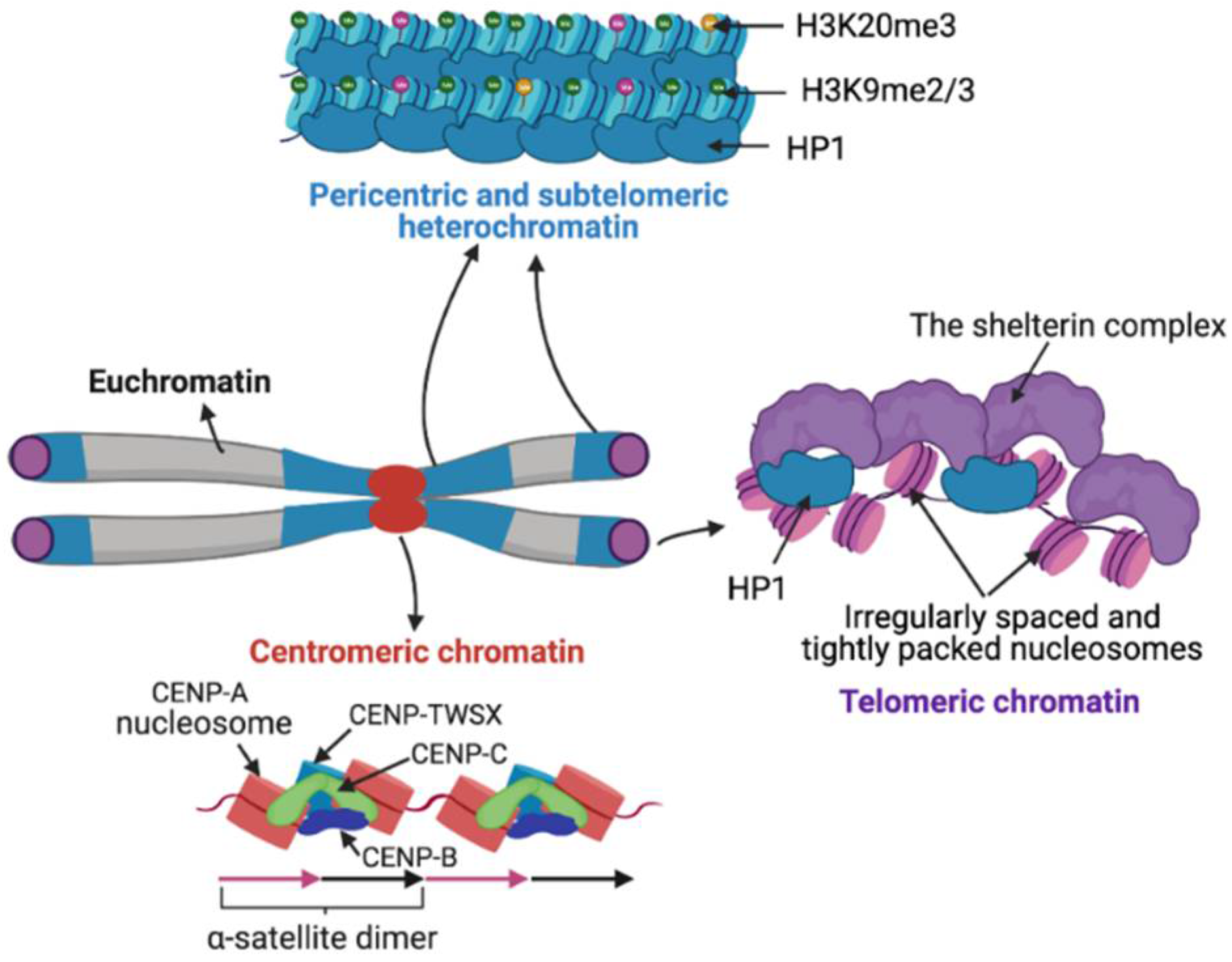
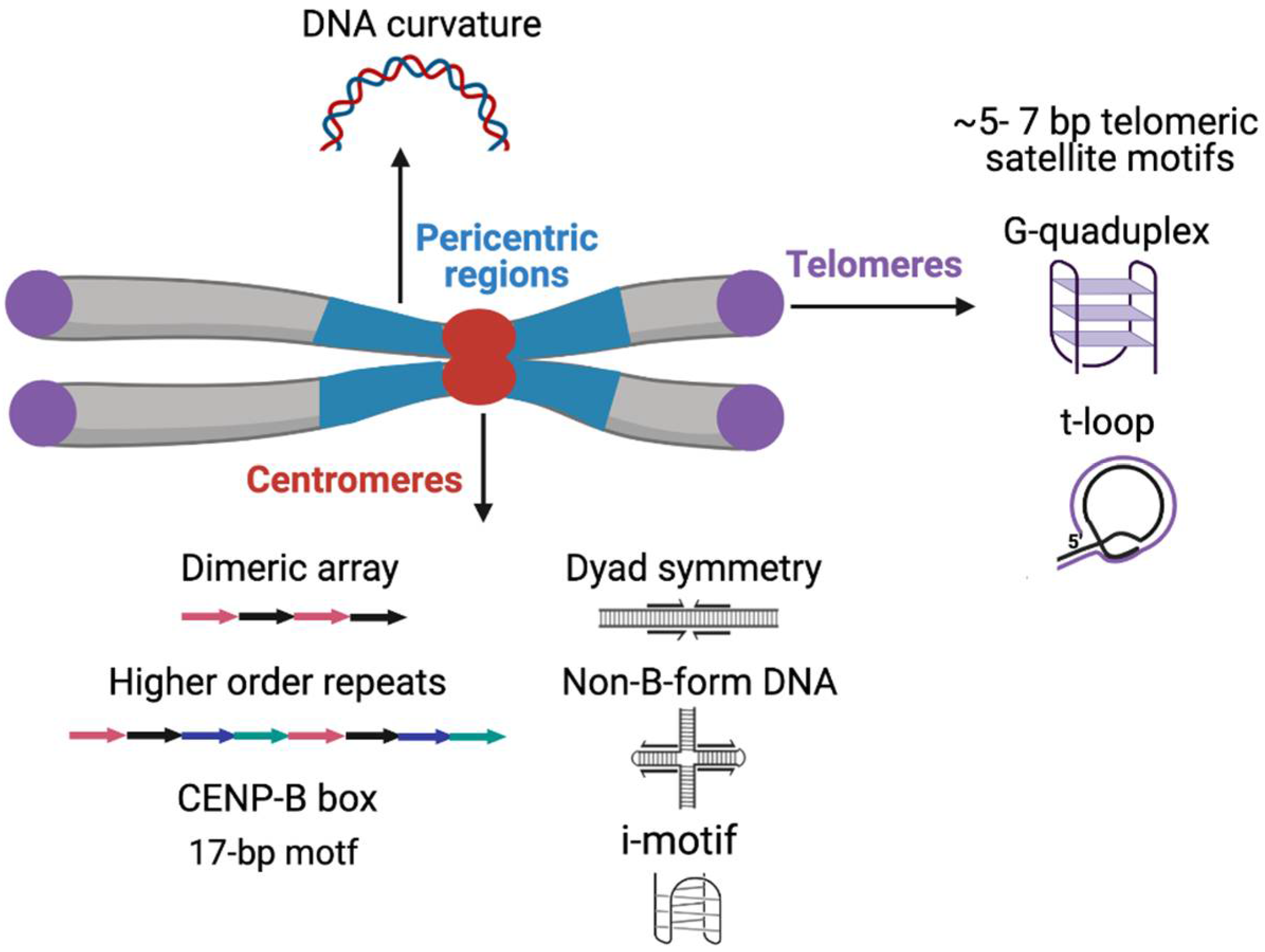
Satellite DNA consists of very large arrays of tandemly repeating, non-coding DNA.Satellite DNA is the main component of functional centromeres, and form the main structural constituent of heterochromatin.. The name "satellite DNA" refers to the phenomenon that repetitions of a short DNA sequence tend to produce a different frequency of the bases adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine, and.
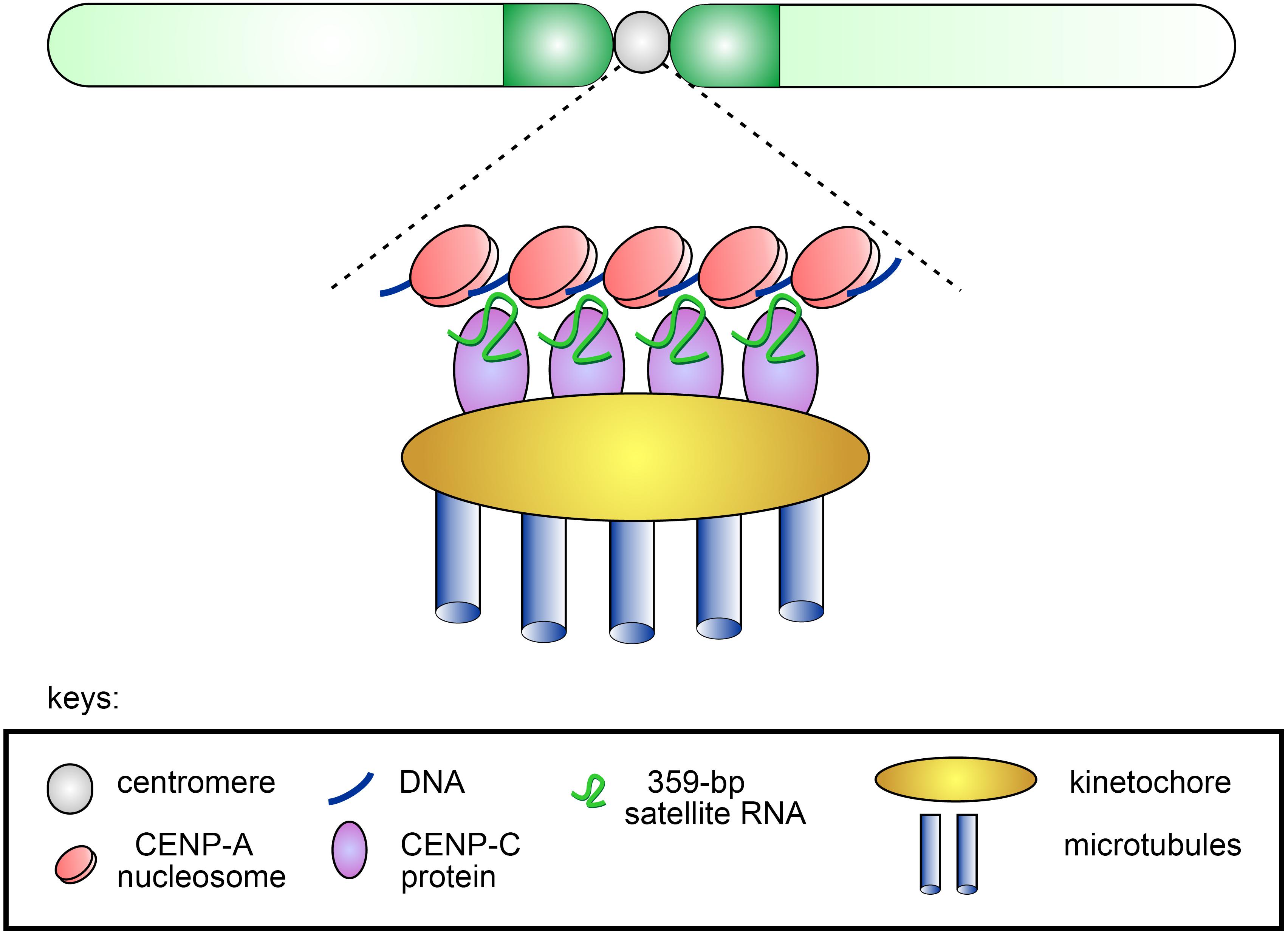
Genomic Organization of Human Centromeres (A) Human centromeres contain... Download Scientific

Simple Sequence Repeat Abundance in Transcribed Regions. Numerous lines of evidence have demonstrated that genomic distribution of simple sequence repeats (SSRs) is nonrandom, presumably because of their effects on chromatin organization, regulation of gene activity, recombination, DNA replication, cell cycle, mismatch repair (MMR) system, etc. (see review, Li et al. 2002).
Satellite DNA, microsatellite (Short Tandem Repeats i.e. STR, SSR), minisatellite, VNTR YouTube

2. Satellite DNA Sequences. Satellite DNAs are classified into microsatellites, minisatellites, satellites and macrosatellites based on the monomeric repeat length. Microsatellites, most relevant to medicine, also called simple sequence repeat (SSR) or short tandem repeat (STR), are small (2-6 bp in size) tandem repeats.
IJMS Free FullText Sequence, Chromatin and Evolution of Satellite DNA
Abstract. Microsatellite repeat DNA is best known for its length mutability, which is implicated in several neurological diseases and cancers, and often exploited as a genetic marker. Less well-known is the body of work exploring the widespread and surprisingly diverse functional roles of microsatellites. Recently, emerging evidence includes.
What is Satellite DNA Microsatellite Minisatellite VNTRs YouTube

RFLP. RFLP is a method by combining the restriction enzyme digestion of the whole genome and southern hybridization with specific probes. It was first used in a criminal case by Dr. Alec Jeffreys with minisatellite marker of human as the probe. The repeat unit of minisatellite DNA (also named VNTR previously) usually ranges from 10 to 100 bp.
The first event is an expansion of microsatellite arrays (red boxes) on... Download Scientific

Other articles where minisatellite DNA is discussed: DNA fingerprinting:.highly variable DNA (known as minisatellites), which do not contribute to the functions of genes, are repeated within genes. Jeffreys recognized that each individual has a unique pattern of minisatellites (the only exceptions being multiple individuals from a single zygote, such as identical twins).
Minisatellites WUR

Tandem Repeat s (Micro-, Mini- and Mega-Satellite) Sequence Definitions. TRs are classified according to their size in repeats with units less than nine nucleotides (nt) in length, which are known as microsatellites, or also as simple sequence repeats (SSRs), or short tandem repeats (STRs), and those with units of 10 nt or greater in length.
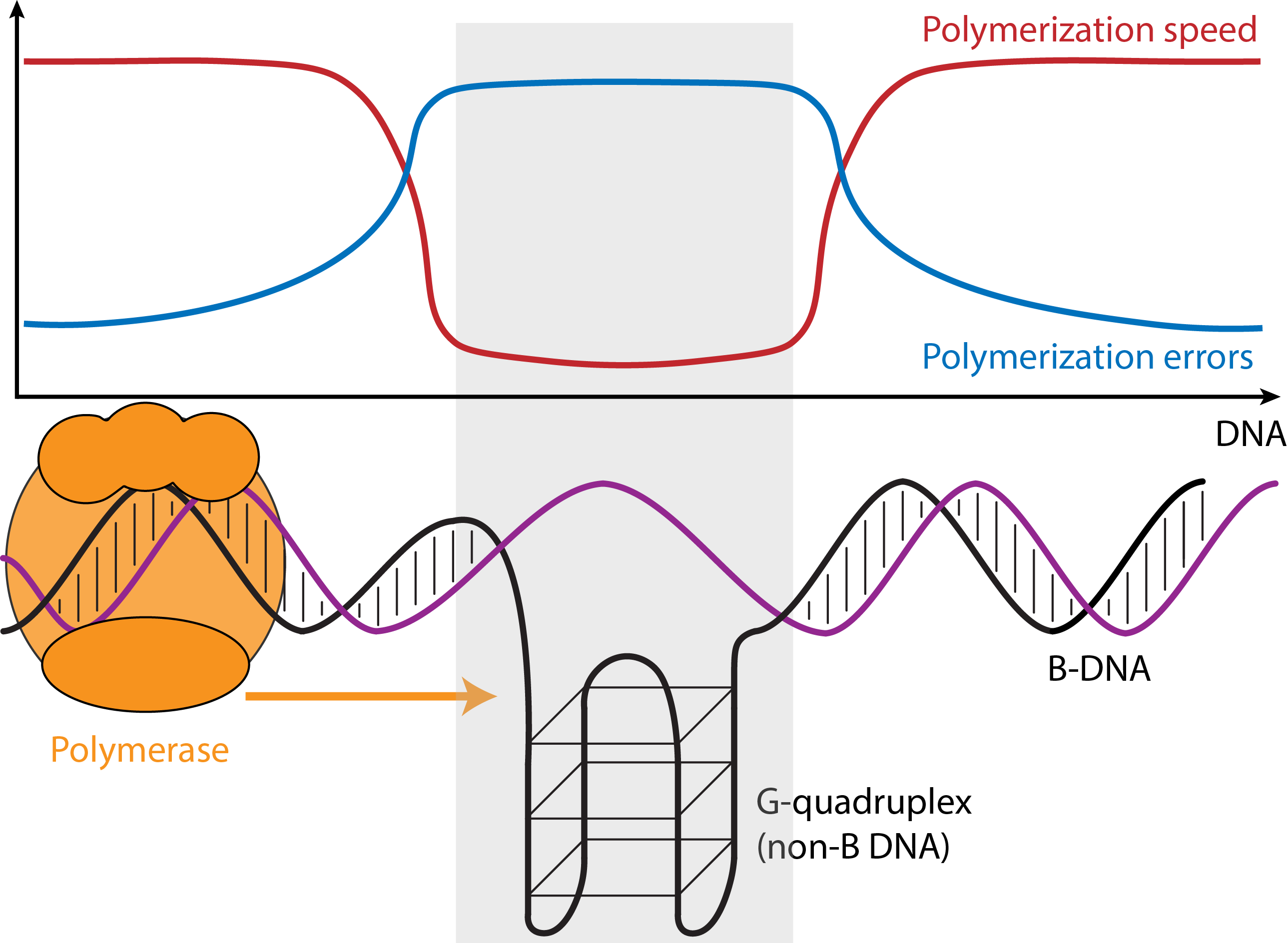
NonB DNA and microsatellite variation and evolution The Makova Lab at Penn State
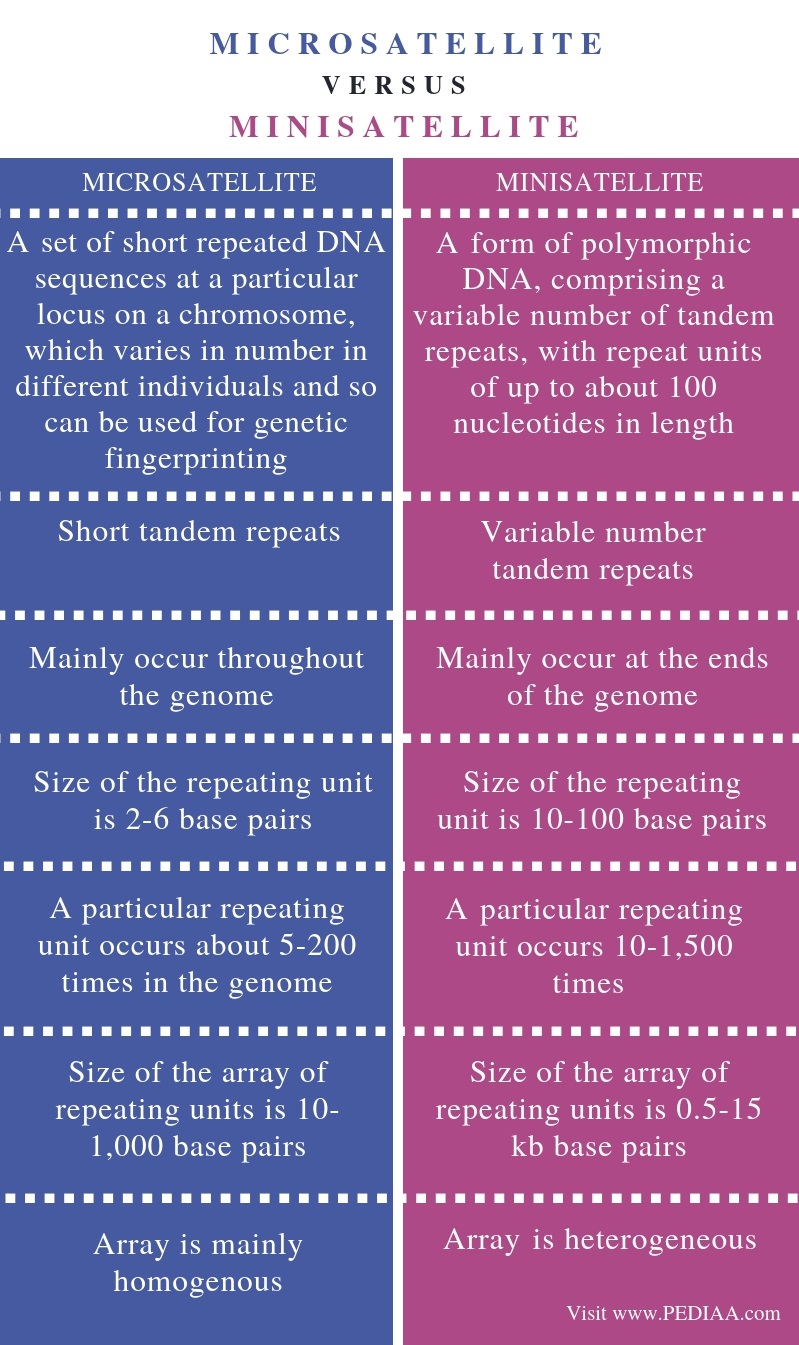
October 17, 2018. by Lakna. 4 min read. The main difference between microsatellite and minisatellite is that the repeating unit of a microsatellite consists of 2-6 base pairs while the repeating unit of a minisatellite consists of 10-100 base pairs. Furthermore, a microsatellite array contains 5-200 repeats while a minisatellite array contains.